Die-casting mold is important to process equipment in die-casting production. The molten metal cools and solidifies in the die-casting mold, and finally forms the die-casting part. The shape, size, quality of die-casting parts, and the smoothness of die-casting production are closely related to die-casting molds. Therefore, it is very important to design die-casting molds correctly and reasonably.
1. Basic structure of die casting mold
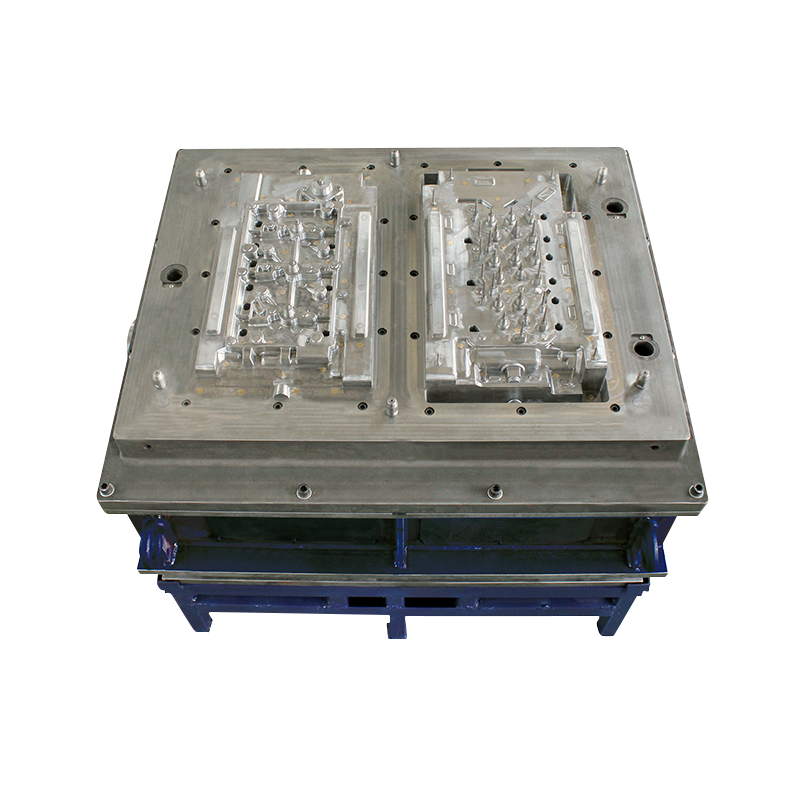
Commonly used die casting molds are composed of two half molds, which are called fixed mold and movable mold. There are also more complex die-casting molds, with more than two mold halves. The components of the die-casting mold are shown in Figure 1.
The functions of the components of the die-casting mold are as follows:
(1) The sprue is connected to the pressure chamber or to the runner, including the sprue sleeve and the diverter cone.
(2) Gating system The channel through which alloy liquid enters the cavity, including sprue, runner, and sprue.
(3) The cavity is formed on the insert to form the geometry of the die casting.
(4) Core pulling mechanism Completes the extraction and insertion of the movable core, including slideways, sliders, oil cylinders, slashes, etc.
(5) Exhaust system Exhaust gas and store cold metal residues, etc.
(6) Temperature control system Controls the temperature of the die-casting mold, including cooling water pipes and heating oil pipes.
(7) Ejector mechanism to eject the die-casting parts from the cavity, including ejector rods, etc.
(8) Moving mold frame Connect and fix moving mold parts, including sleeve plate, support plate, etc.
2. Design of die-casting mold
The following points should be paid attention to when designing a die-casting mold:
(1) It is necessary to adopt an advanced and simple structure as much as possible to ensure stable and reliable operation and daily maintenance and repair.
(2) The modifiability of the gating system should be considered, and necessary modifications can be made during the debugging process.
(3) Reasonable selection of various tolerances, scales, and machining allowances to ensure reliable module coordination and required to die casting accuracy.
(4) Select appropriate mold materials and a reliable heat treatment process to ensure the service life of die-casting molds.
(5) It should have sufficient rigidity and strength to withstand the clamping pressure and expansion force without deformation during the die-casting production process.


 Pусский
Pусский Español
Español